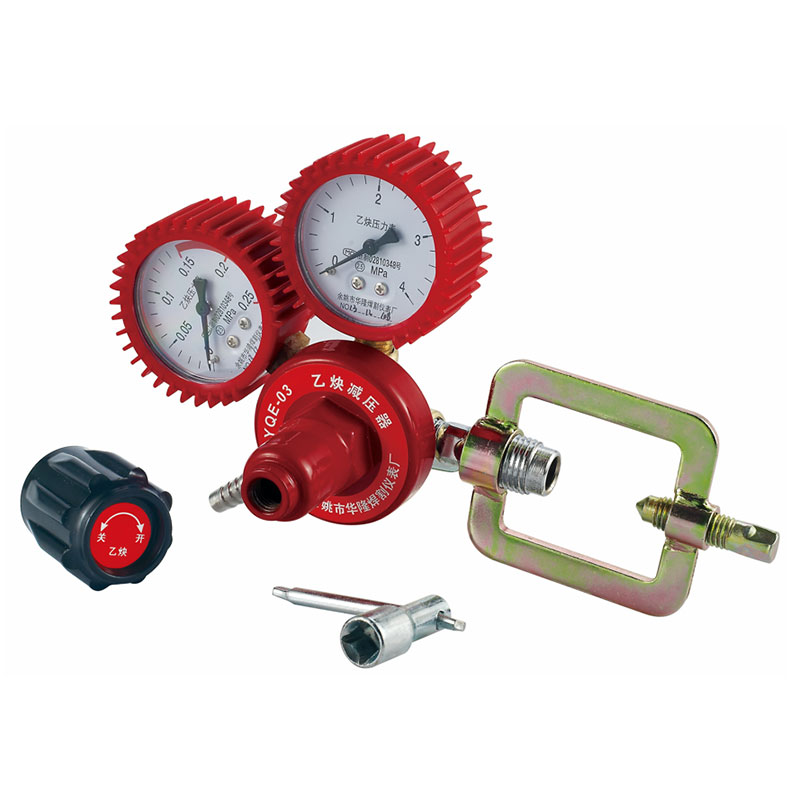
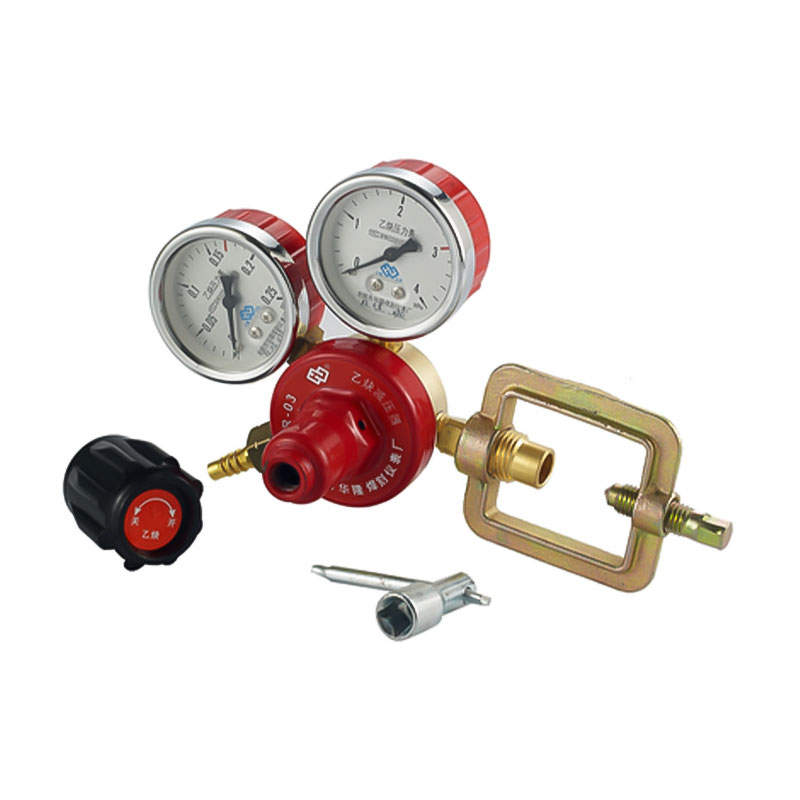
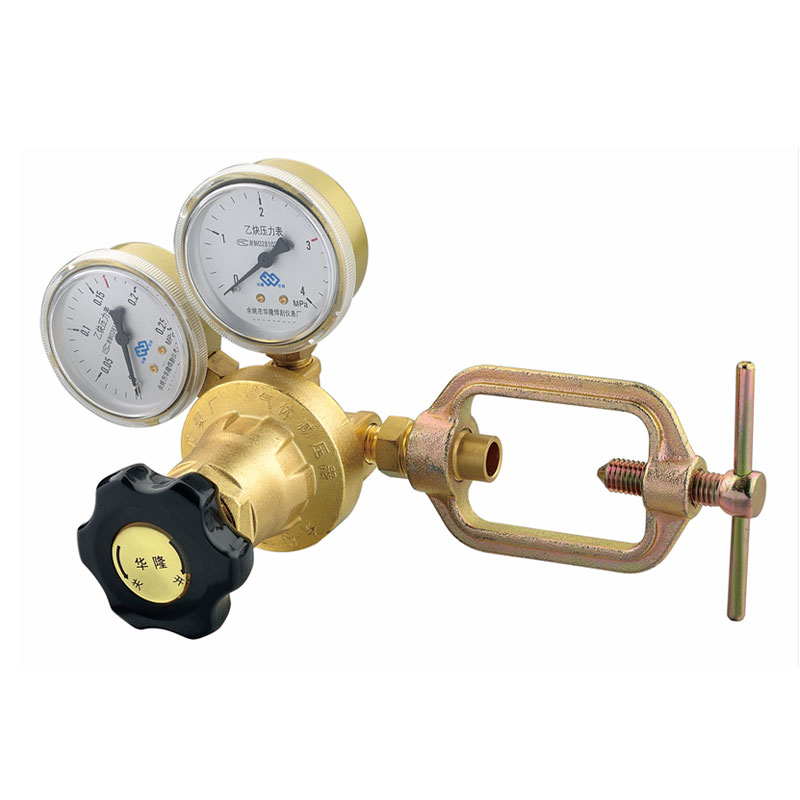
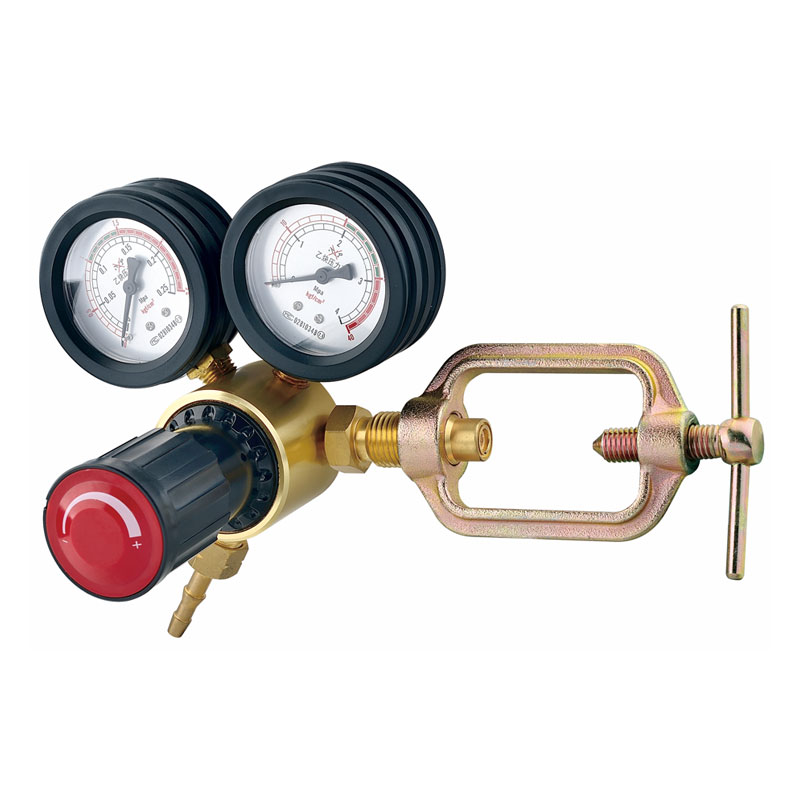
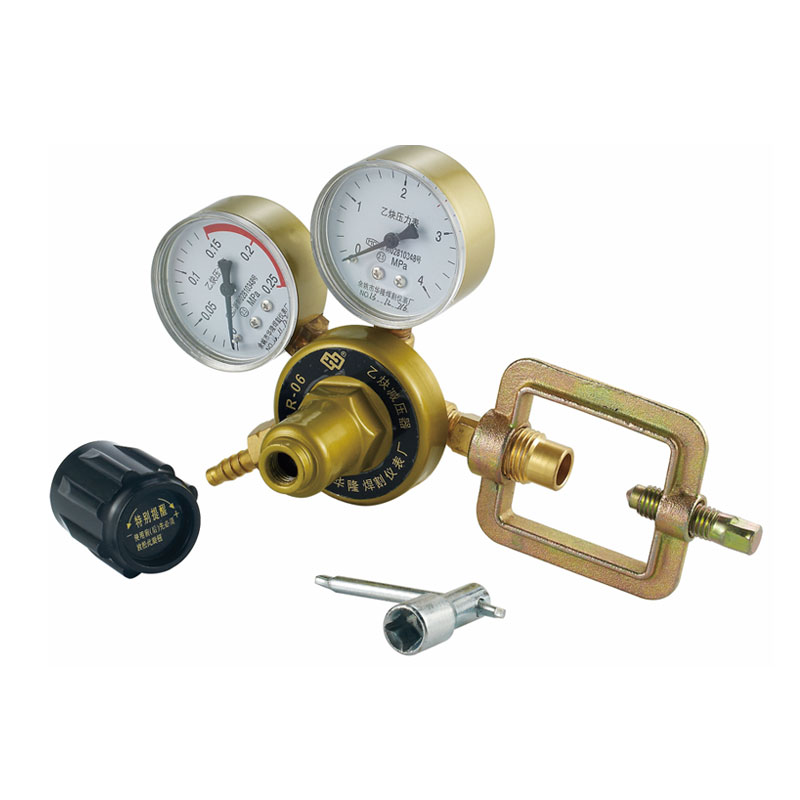
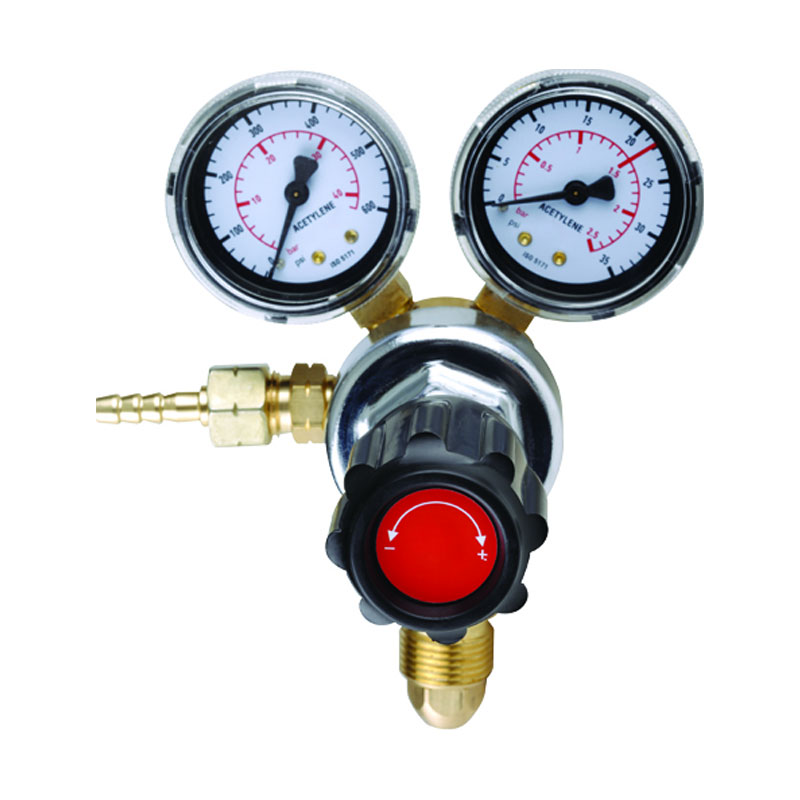
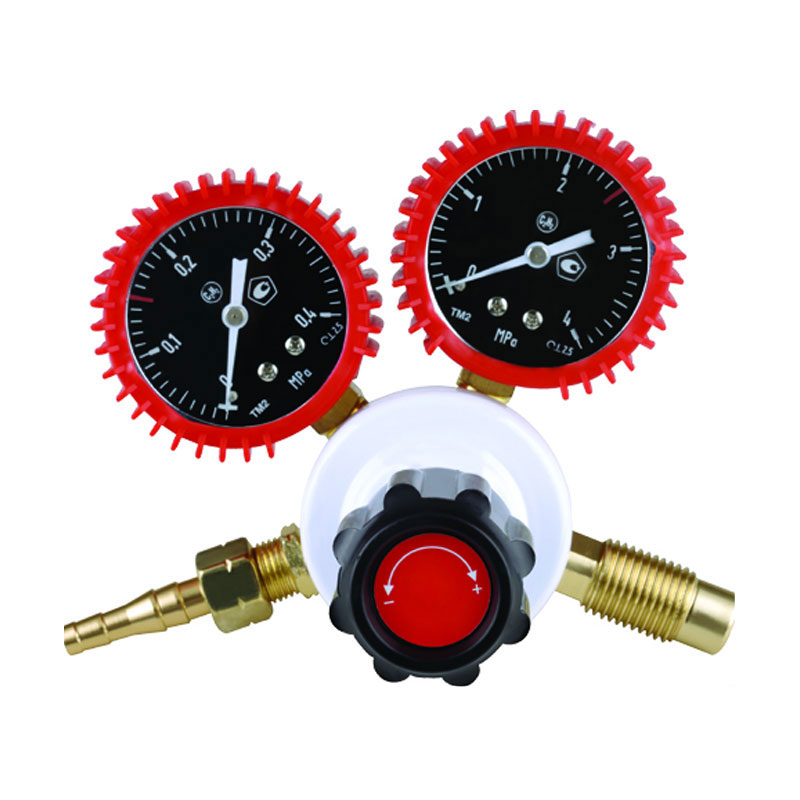
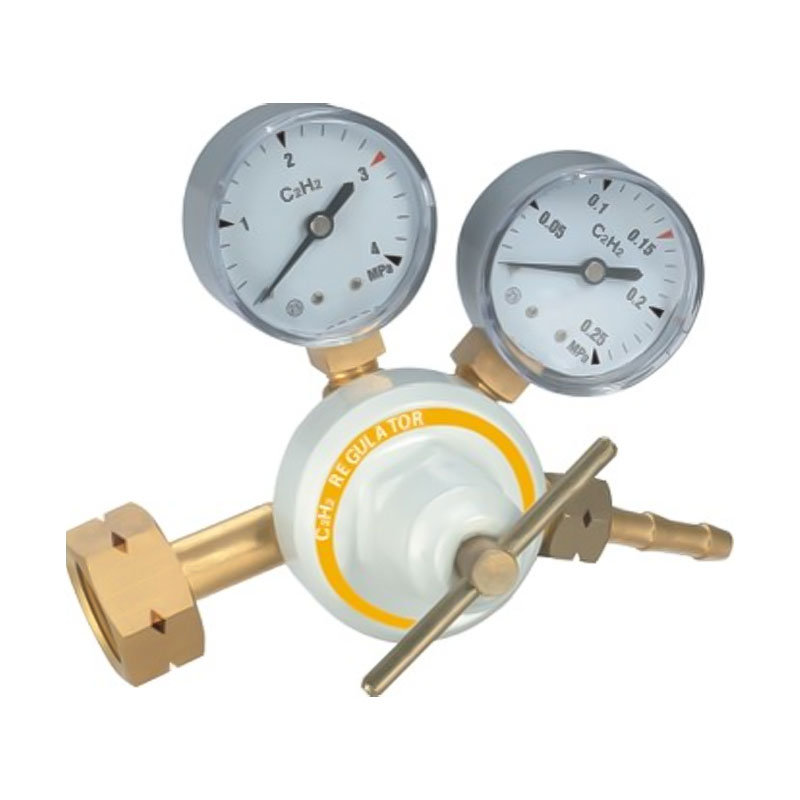
Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory. was established in 2007 as China Pressure Regulator for Welding and Cutting Manufacturers and Custom Pressure Regulator for Welding and Cutting Suppliers specializing in the R&D, production, and sales of industrial pressure regulators. The company is equipped with advanced production and testing facilities, and its products are widely used in industries such as petroleum and chemicals, welding and cutting, beer and beverages, aquatic plant landscaping, and aquaculture, earning broad trust from customers worldwide due to their exceptional quality and reliable performance.
Adhering to the business philosophy of "Innovation-Driven, Quality-Oriented", we have established a comprehensive quality management system. Our R&D team continuously optimizes product designs, launching multiple energy-efficient, safe, and reliable Pressure Regulator to meet diverse operational requirements. Meanwhile, we provide professional technical support and after-sales services.
Looking ahead, we will continue to deepen our expertise in the gas regulator sector driving industry advancement through technological innovation. We are committed to becoming a leading global provider of pressure regulator solutions.
Product
Pressure Regulator for Welding and Cutting Manufacturers
Learn about our industry exhibition information and recent events in our company.
The Critical Role of Pressure Regulators in Welding and Cutting
Welding and cutting are core industrial processes that rely on precise gas control. In these applications, gases are typically stored in high-pressure cylinders, with pressures reaching 2200 psi or even higher. However, the actual working pressure and flow required for welding and cutting operations are much lower (for example, the working pressure for acetylene cutting is usually below 15 psi, and shielding gas flow may be between 10 L/min and 25 L/min). This significant pressure differential makes the pressure regulator for welding and cutting an indispensable component for safe and efficient operation.
The core function of the pressure regulator is to perform two key tasks:
- Pressure Reduction: To reduce the dangerously high pressure inside the cylinder to a safe and controllable working pressure.
- Pressure Stabilization: To maintain the set outlet pressure and flow rate stably, even as the pressure inside the cylinder continuously drops with gas consumption.
Safety and Efficiency
Using a qualified welding and cutting pressure regulator is the primary condition for ensuring the safety of operators and the working environment. Uncontrolled pressure can lead to hose rupture, flashbacks, or even more serious accidents. From an efficiency perspective:
- Optimizing Gas Consumption: Precise control of gas flow, particularly for expensive shielding gases (such as argon and helium), can significantly reduce waste and lower running costs.
- Improving Process Quality: A stable gas supply is vital for achieving high-quality welds or clean cuts. Unstable gas flow can result in inadequate shielding gas coverage, leading to weld porosity, oxidation, or rough cut surfaces.
Since its establishment in 2007, Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory, as a manufacturing enterprise specializing in the R&D, production, and sales of industrial pressure regulators, has been committed to providing products that guarantee the safety and quality of welding and cutting. Adhering to the business philosophy of "Innovation-Driven, Quality-Oriented", the company has established a comprehensive quality management system, ensuring that the manufactured pressure regulators possess exceptional quality and reliable performance, earning broad trust from customers worldwide.
I. How Welding and Cutting Pressure Regulators Work
Core Function Analysis
The welding and cutting pressure regulator is essentially an automatic control valve, with its core task being the achievement of constant pressure output through mechanical balance. It receives the input pressure (Pin) from the high-pressure cylinder and reduces it to a user-set and stable output pressure (Pout).
The regulator's structural design allows it to use feedback from the outlet pressure to automatically adjust the flow of high-pressure gas entering the low-pressure chamber.
Internal Mechanism
The precise control of the pressure regulator primarily relies on the interaction of the following three key components:
- Spring:
- Function: The user rotates the adjusting knob to compress the spring, presetting the desired outlet pressure. The force exerted by the spring pushes the diaphragm to open the main valve, allowing gas to flow in.
- Diaphragm:
- Function: Usually made of a flexible material (such as synthetic rubber or metal), it is the core component for pressure sensing. One side of the diaphragm is subject to the set pressure force from the spring, and the other side is subject to the feedback force from the outlet gas pressure (Pout).
- Balance: When the outlet pressure increases, the gas pressure on the diaphragm increases, overcoming the spring force and partially closing the main valve. When the outlet pressure decreases, the spring force dominates, the diaphragm opens the main valve, allowing more gas to flow in, thus maintaining a dynamic balance.
- Seat and Valve Stem:
- Function: This is the inlet for gas into the low-pressure chamber. The precise opening or closing of the valve seat is controlled by the diaphragm based on pressure feedback.
Through this precise internal mechanism, pressure regulators manufactured by companies like Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory are able to achieve accurate control of Pout, ensuring their products play a critical role in petrochemical, welding and cutting, and other industrial applications. The company is equipped with advanced production and testing facilities, continuously optimizing product designs to ensure its pressure regulators are energy-efficient, safe, and reliable choices.
Pressure Gauge Functions
High-quality welding and cutting pressure regulators are typically equipped with two separate pressure gauges:
| Parameter Comparison | Inlet Pressure Gauge | Outlet Pressure Gauge |
| Function | Displays the remaining high pressure inside the cylinder, used for monitoring gas inventory. | Displays the user-set working pressure (or flow rate, if it is a flowmeter regulator). |
| Range | Typically has a large range (e.g., 0 psi to 4000 psi). | Has a smaller range to improve reading accuracy (e.g., 0 psi to 100 psi). |
| Connection Location | High-pressure chamber near the cylinder connection. | Low-pressure chamber near the hose connection. |
| Criticality | Used to plan working time and avoid sudden gas depletion. | Used to accurately set the required process parameters for welding/cutting. |
II. Different Types of Welding and Cutting Pressure Regulators
When selecting a pressure regulator for welding and cutting, it is crucial to understand the main types and their operating characteristics. The gas regulators on the market are mainly divided into single-stage and two-stage categories, which differ significantly in pressure stability, cost, and applicability.
Single-Stage Regulator
A single-stage pressure regulator reduces the cylinder pressure to the desired working pressure in a single step.
| Feature Comparison | Single-Stage Regulator | Two-Stage Regulator |
| Pressure Reduction Process | One step of reduction | Two steps of reduction (from cylinder pressure to intermediate pressure, then to working pressure) |
| Outlet Pressure Stability | Fluctuates as cylinder pressure drops (requires manual adjustment) | Extremely high, output pressure remains constant |
| Structural Complexity | Simple structure, usually smaller size | Complex structure, usually larger size |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Application | Short-duration, intermittent, or non-precision flame cutting/welding operations. | Long-duration, continuous, or high-precision TIG/MIG welding. |
- Pros and Cons Analysis: The main advantages of single-stage regulators are their simple structure, small size, and low cost. However, because the outlet pressure is directly affected by the drop in cylinder pressure, operators must frequently manually adjust the regulating knob during prolonged work to maintain constant working pressure.
- Typical Application: Suitable for those welding and cutting tasks that are less sensitive to pressure fluctuations or have shorter operation times, such as small-scale oxy-acetylene cutting.
Two-Stage Regulator
The two-stage pressure regulator achieves excellent pressure stability, and is the ideal choice for high-precision welding and cutting.
- Working Principle: The gas first enters a primary stage chamber, reducing the high pressure to a fixed intermediate pressure (e.g., 200 psi). The gas then enters a secondary stage chamber, where the intermediate pressure is precisely reduced to the required working pressure.
- Pros and Cons Analysis: Although two-stage regulators have higher manufacturing costs and selling prices, their core advantage is providing extremely stable gas delivery. This stability is crucial for ensuring weld consistency and minimizing rework. The R&D team at Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory continuously optimizes product designs to ensure its two-stage pressure regulators deliver excellent constant-pressure performance, meeting the stringent demands of customers under prolonged, high-load work.
Gas Specificity and Safety Considerations
Pressure Regulators For Welding And Cutting must be specifically designed for the gas they use, which is not only a matter of performance but also of safety.
| Gas Type | Typical Application | CGA Fitting Standard | Safety/Structural Characteristics |
| Oxygen (O2) | Flame cutting, oxy-fuel welding | CGA 540 | Right-hand thread connection, strictly forbids oil and grease. |
| Acetylene (C2H2) | Oxy-fuel welding, flame cutting preheat | CGA 510 | Left-hand thread connection (to prevent improper connection); maximum safe working pressure ≤ 15 psi. |
| Argon (Ar) / Helium (He) / Ar/CO2 Mix | TIG/MIG Welding shielding gas | CGA 580 | Usually integrates a Flowmeter rather than a pressure gauge for precise flow control. |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | MIG Welding shielding gas | CGA 320 | Requires a Heater to prevent freezing inside the regulator due to gas expansion and cooling. |
Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory strictly adheres to international safety standards and CGA specifications in the R&D and production of industrial pressure regulators. It offers specialized regulators with precisely matched fittings and safety relief devices to address the diverse gas needs in industries such as petrochemicals and welding and cutting. The company is committed to providing energy-efficient, safe, and reliable pressure regulator solutions that meet various operational requirements through continuous technological innovation.
III. Key Factors for Choosing the Right Welding and Cutting Pressure Regulator
Selecting a safe, efficient, and durable pressure regulator for welding and cutting is a prerequisite for successful operation. Users must carefully evaluate the regulator's compatibility, flow capacity, material, and safety features to ensure it meets specific process requirements.
Gas Compatibility and Safety
The compatibility of the pressure regulator with the gas used is the most crucial factor among all selection criteria. Different gases have unique chemical properties, pressure characteristics, and potential hazards, so regulator design must strictly adhere to the principle of gas specificity.
- CGA Fitting Standards: The Compressed Gas Association (CGA) in the US has established industry standards, assigning specific fitting sizes and thread directions to each gas. This is the main safety mechanism to prevent users from mistakenly connecting an oxygen regulator to an acetylene cylinder. For example, flammable gas (like acetylene) fittings typically use left-hand threads, while non-flammable gases (like oxygen) use right-hand threads.
- Risks of Incompatibility: Connecting an incompatible regulator to a cylinder can lead to catastrophic consequences, such as:
- High-Pressure Damage: Connecting a low-pressure gas (like acetylene) regulator to a high-pressure cylinder can cause the regulator to rupture.
- Fire/Explosion: Contact between oxygen and oil/grease or incompatible sealing materials inside the regulator can cause spontaneous combustion or explosion.
Guided by its philosophy of "Innovation-Driven, Quality-Oriented," Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory ensures that all its pressure regulator products strictly comply with the relevant CGA standards and gas compatibility requirements. The company provides professional technical support to guide customers in selecting the correct gas regulator model to meet the purity and safety needs of various gases.
Pressure and Flow Matching
The regulator's flow capacity must be able to meet the maximum gas consumption rate required by the welding and cutting application.
- Flow Rate:
- For shielding gases (such as argon, Ar/CO2 mix), flow is usually measured in cubic feet per hour (CFH) or liters per minute (LPM). For instance, MIG welding might require a shielding gas flow of 15 L/min to 25 L/min.
- Users should select a pressure regulator or a regulator with an integrated flowmeter whose maximum flow output exceeds the peak flow required by the application.
- Delivery Pressure: The regulator must be able to stably provide the set working pressure required by the application. For example, for high-pressure oxygen cutting of thick plates, a higher outlet pressure may be required to drive the nozzle.
| Parameter | Flow Rate | Delivery Pressure |
| Function | Ensures sufficient gas volume is supplied to the torch or cutting nozzle. | Ensures the gas reaches the work area with the correct force. |
| Selection Criteria | Must be greater than or equal to the peak flow required by the process. | Must be able to stably maintain the working pressure required by the process. |
| TIG Welding Reference | Typically 8 L/min to 15 L/min. | Typically 20 psi to 50 psi. |
| Flame Cutting Reference | Depends on nozzle size and metal thickness. | Above 50 psi, or even higher. |
Materials and Durability
The regulator's construction material directly affects its durability, safety, and resistance to specific gases.
- Brass: This is the most common and standard material for Pressure Regulators For Welding And Cutting because of its excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and good compatibility with oxygen, acetylene, and inert gases.
- Stainless Steel: Primarily used for high-purity, highly corrosive gases, or applications requiring the highest cleanliness, such as in the petroleum and chemical industry or certain precision TIG welding applications.
- Diaphragm Material: High-quality synthetic rubber or metallic diaphragms are crucial for ensuring the long-term stability of the pressure regulator.
Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory, in the production of pressure regulators, strictly selects high-quality brass and stainless steel, ensuring the products can withstand harsh industrial environments and provide reliable long-term performance. The company's advanced production and testing facilities guarantee the durability and reliability of every component.
Safety Features
A high-quality gas regulator must integrate several protective mechanisms:
- Pressure Relief Valve (PRV): A critical safety device. If the internal pressure overshoots due to a fault (such as a worn valve seat), the PRV automatically vents the excess gas to prevent the regulator body from rupturing.
- Sintered Filter: Usually located at the high-pressure inlet of the regulator. Its function is to filter impurities and particles from the gas flow, protecting the internal valve seat and diaphragm from physical damage, thereby extending the service life of the pressure regulator.
IV. Safe Installation and Operation Procedures for Welding and Cutting Pressure Regulators
Even with the highest quality pressure regulator for welding and cutting, improper installation and operation can lead to gas leaks, pressure loss, or even serious safety incidents. Therefore, strictly following safe installation and operation procedures is paramount.
Installation Steps
The process of installing a pressure regulator must be performed carefully to ensure the integrity and cleanliness of the connection:
- Preparation and Inspection: Before connecting the regulator, quickly open the cylinder valve briefly (known as "cracking" or "flicking") for a few seconds. This is intended to blow out dust, dirt, or impurities from the valve outlet.
- Warning: Never stand directly in front of the valve outlet during this operation, and ensure no one is nearby.
- Check Connection Cleanliness: Check the inlet connection of the pressure regulator and the cylinder valve outlet to ensure there is no grease, oil, or any foreign matter, especially for oxygen regulators. Any contamination in contact with high-pressure oxygen can lead to combustion or explosion.
- Install the Regulator: Ensure the adjusting knob is completely loosened (turned counter-clockwise all the way), which is the zero-pressure setting. Hand-tighten the regulator into the cylinder valve, confirming that the CGA fitting matches correctly.
- Tighten the Connection: Use the correct open-end wrench to tighten the regulator connection. It must be tightened to the manufacturer's recommended torque to ensure a gas seal, but never overtighten, which could damage the threads or cause the washer to fail.
Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory considers ease of installation in its product design and provides detailed installation instructions to users. The company's comprehensive quality management system ensures the cleanliness and precision of the fitting area for every regulator leaving the factory.
Key Post-Installation Step: Leak Testing
After installation, and once the cylinder valve is opened, a leak test must be performed to verify that all connections are perfectly sealed.
| Leak Testing Procedure | Description | Safety Importance |
| Step 1: Pressurization | Ensure the gas valve on the torch or cutting nozzle is closed, then slowly open the cylinder valve to apply pressure to the pressure regulator and the downstream line. | Slowly opening the cylinder valve prevents gas flow shock from damaging the regulator's internal components. |
| Step 2: Testing | Apply a specialized leak detection fluid or soapy water solution around all fittings, hoses, and the regulator body. | The appearance of soap bubbles is a clear indication of a gas leak. |
| Step 3: Adjustment | If a leak is found, immediately close the cylinder valve, release the residual gas, re-check and tighten the connection, and then retest. | Any leak must be completely eliminated before beginning welding and cutting operations. |
Correct On/Off Procedure
Following the correct sequence of operations extends the lifespan of the welding and cutting pressure regulator and prevents hazardous situations:
- Start-Up Procedure:
- Regulator knob is loose (zero pressure).
- Slowly open the cylinder main valve (to prevent high-pressure shock).
- Observe the high-pressure gauge to confirm cylinder pressure.
- Slowly adjust to the required working pressure using the regulating knob.
- Shut-Down Procedure:
- Close the cylinder main valve.
- Allow the gas to continue flowing out or open the torch/welding gun valve until the readings on both the high-pressure and low-pressure gauges on the pressure regulator drop to zero. This process is called "bleeding" or "depressurizing."
- Loosen the adjusting knob, returning it to the zero-pressure position.
Daily Safety Tips
- Cylinder Securing and Storage: Cylinders must always be upright and securely fastened using chains, clamps, or safety cages to prevent tipping.
- Avoid Oil/Grease: Any grease, oil, lubricant, or fat is strictly forbidden from coming into contact with the oxygen pressure regulator or cylinder valve.
- Inspection: Periodically inspect the gas regulator body, gauges, and all connections for signs of wear, damage, scratches, or corrosion. If the regulator has suffered a severe impact or drop, it should be professionally safety-checked even if no visible damage is present.
Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory is committed to becoming a leading global provider of pressure regulator solutions. It not only provides safe and reliable products through technological innovation but also offers professional after-sales service and technical support to help customers understand and follow the most stringent welding and cutting safety guidelines.
V. Maintenance and Common Troubleshooting for Welding and Cutting Pressure Regulators
Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring the long-term stability and safety of the pressure regulator for welding and cutting. Since the gas regulator is a precision instrument, regular inspection and maintenance can effectively extend its service life and prevent potential hazards.
Preventive Maintenance
For any welding and cutting pressure regulator, preventive maintenance should adhere to the following basic principles:
- Daily Inspection:
- Check that the pressure gauge pointers return to zero, ensuring no residual pressure is incorrectly read.
- Check the exterior of the regulator for visible physical damage, such as casing cracks, deformed fittings, or broken gauge glass.
- Ensure the adjusting knob turns smoothly, without sticking or excessive looseness.
- Regular Leak Testing: Even regulators in normal use should be checked for leaks (e.g., quarterly) using leak detection fluid on all connection points to prevent minor leaks from developing into serious problems over time.
- Replacing Consumables: Hoses and seals are consumables. They should be replaced immediately if they show signs of hardening, cracking, or aging.
Determining Replacement Timing
The pressure regulator is not a permanent piece of equipment. As internal components (such as valve seats, diaphragms, and springs) wear out over time and use, the regulator will eventually need replacement.
| Failure Symptom | Potential Cause | Is Regulator Replacement Necessary? |
| Pressure Creep (Outlet pressure continuously rising) | Worn valve seat or contamination stuck inside, causing gas to continuously leak into the low-pressure chamber. | Yes. This is a sign of internal seal failure and compromises safety. |
| Severe External Damage | Regulator dropped, leading to serious deformation of the casing, gauge, or fittings. | Yes. Even if superficially intact, internal precision and structural integrity may be compromised. |
| Unstable Output | Even when cylinder pressure is stable, output pressure fluctuates sharply. | Usually yes. May indicate severe fatigue of the spring or diaphragm. |
| Leak at Connection Point | Only the sealing washer is worn. | No. Can be fixed by replacing the washer or O-ring. |
Guided by the philosophy of "Innovation-Driven, Quality-Oriented," Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory continuously optimizes the durability of its internal regulator components. However, for operational safety, the company advises that the regulator be immediately taken out of service or sent to a professional facility for repair if any critical failure (such as pressure creep) is detected.
Common Troubleshooting Guide
Here are common problems that may be encountered when using a welding and cutting pressure regulator and their solutions:
- Problem 1: Outlet Pressure Continuously Rises (Pressure Creep)
- Cause: Wear or dirt between the regulator's main valve seat and stem, preventing the valve from closing tightly.
- Solution: Stop use immediately and follow the safe shut-down procedure (close cylinder first, then bleed). Due to the precise internal components, user disassembly is not recommended.
- Problem 2: Insufficient Gas Flow / Pressure Below Setpoint
- Cause:
- Cylinder pressure is too low (check the high-pressure gauge).
- Partial blockage in the line or torch/cutting nozzle.
- Regulator capacity is insufficient to meet the high demands of the welding and cutting operation.
- Solution: Check remaining cylinder pressure; clean downstream equipment. If the regulator capacity is insufficient, a model with a larger capacity needs to be used.
- Cause:
- Problem 3: Bubbles at the Connection Point (Leak)
- Cause: CGA fitting is not tightened sufficiently, or the sealing washer/O-ring is damaged or missing.
- Solution: Immediately close the cylinder, release the pressure. Inspect and replace the washer, then retighten the connection and perform the leak test again.
Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory, as a professional pressure regulator manufacturer, is committed to providing reliable pressure regulator solutions and offers professional technical support and after-sales service to guide customers in correct maintenance and fault diagnosis, ensuring the continuous and stable operation of its products in industries such as petroleum and chemicals, and welding and cutting.
FAQ
What is the performance difference between single-stage and two-stage regulators in TIG welding?
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding has extremely high requirements for the purity and stability of the shielding gas.
- A Two-Stage Regulator is the preferred choice for TIG welding. It provides an extremely stable gas flow rate, ensuring the continuity and consistency of the shielding gas coverage even as the cylinder pressure drops, thereby preventing weld oxidation and porosity.
- A Single-Stage Regulator's output pressure will fluctuate with changes in cylinder pressure, which can lead to unstable weld quality, especially during prolonged, precise welding operations.
How to safely release residual gas from a welding and cutting pressure regulator?
Safely releasing residual gas is a standard procedure at the end of every work session, known as "bleeding" or "depressurizing."
- Close the Gas Source: First, thoroughly close the main valve on the cylinder.
- Release Pressure: Safely vent the gas in the hose and the low-pressure chamber of the pressure regulator by opening the gas control valve on the downstream equipment (such as the torch or welding gun).
- Confirm Zero: Once both the high-pressure and low-pressure gauges read zero, the gas has been fully released. At this point, completely loosen the pressure regulator's adjusting knob (turn counter-clockwise all the way), returning it to the zero-pressure setting.
What is the average service life of a gas regulator?
High-quality Pressure Regulators For Welding And Cutting (such as those produced by Yuyao Hualong Welding Meter Factory following high standards) generally have a long service life, but this depends on usage frequency, gas type, and maintenance.
- Under normal industrial use and good maintenance, a regulator can typically be used for 5 to 10 years.
- However, once critical signs of failure, such as continuous pressure creep or irreparable external damage, appear, the regulator must be immediately taken out of service and replaced, regardless of its age.
Why does my flowmeter always show low flow, even if the cylinder is full?
If the high-pressure gauge shows the cylinder is full, but the flowmeter or low-pressure gauge reading is abnormally low, possible causes include:
- Adjusting Knob Not Tightened: The adjusting knob was not screwed in sufficiently counter-clockwise to set an adequate working pressure.
- Downstream Blockage: The hose or the nozzle/gas diffuser inside the torch/welding gun may be partially blocked.
- Sintered Filter Blockage: The high-pressure sintered filter located at the inlet of the pressure regulator may be clogged by impurities in the gas, restricting the flow entering the regulator.
- Incorrect Regulator Sizing: The maximum flow capacity of the regulator is insufficient to meet the consumption demands of the current welding and cutting process.


 English
English  русский
русский  Español
Español