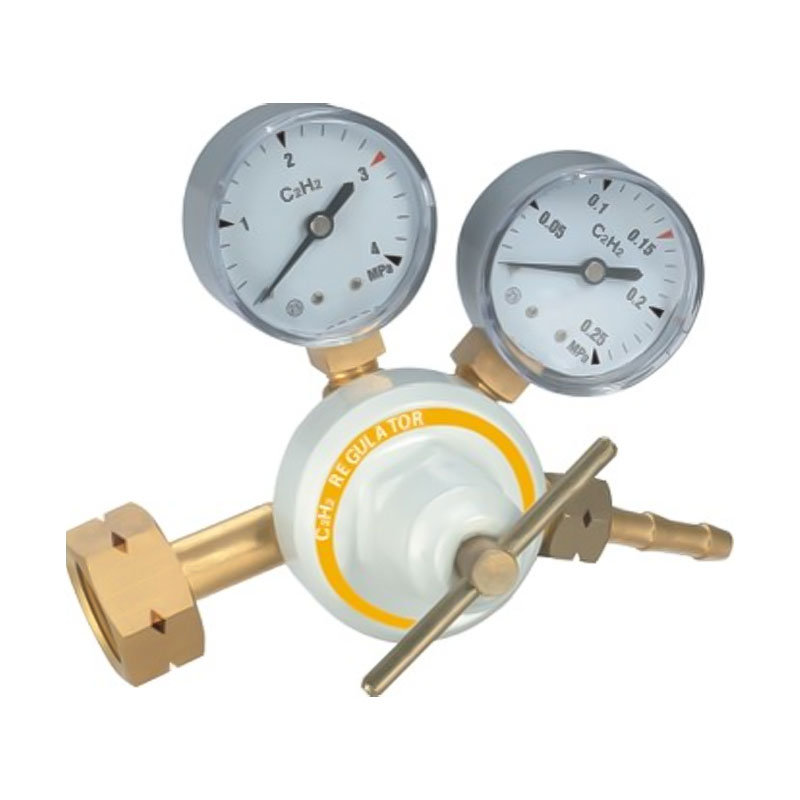
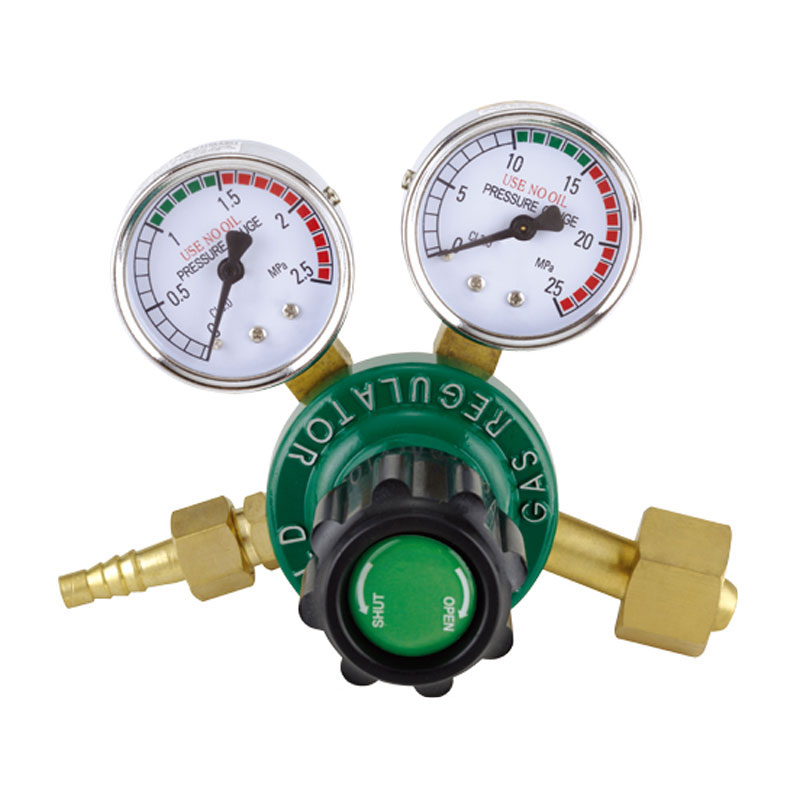
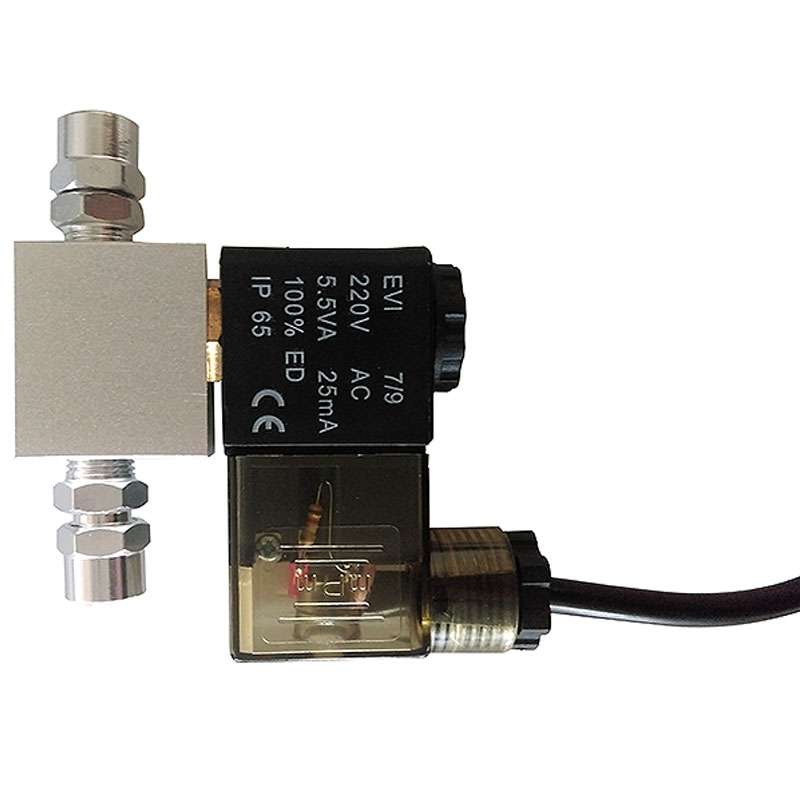
The AR-56 High-Stability Welding and Cutting Acetylene Regulator is designed with a focus on pressur...
See DetailsWhy Is a Pressure Regulator Essential for Welding and Cutting Processes?
Industry News-Welding and cutting are intricate processes that require precise control over gas flow and pressure to ensure quality, safety, and efficiency. The pressure regulator is one of the most critical components in this equation, as it helps maintain the correct gas pressure throughout the operation.
1. Ensures Stable Pressure
Welding and cutting processes, such as oxy-fuel welding, rely on gases like oxygen, acetylene, and argon, which must be delivered at stable, consistent pressures to perform optimally. The internal pressure in gas cylinders can fluctuate based on the amount of gas left, temperature changes, or external factors. Without a pressure regulator, this variability can lead to inconsistent gas flow, resulting in inefficient or even dangerous working conditions.
A pressure regulator stabilizes the gas pressure, ensuring that the flow remains constant regardless of the cylinder’s pressure fluctuations. This stability is vital for processes like welding, where the gas must be at a specific pressure to achieve the desired heat output and weld characteristics.
Key Benefits of Stable Pressure:
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced Variability | Consistent pressure reduces fluctuations that could affect the heat input, improving weld quality and consistency. |
| Increased Process Control | Stable pressure provides better control over the welding or cutting process, ensuring uniformity and precision. |
| Optimized Gas Flow | Ensures that the gas flows smoothly, reducing the risk of under- or over-pressurization, which could affect the operation or safety. |
2. Improves Safety
Safety is paramount in welding and cutting operations. Fluctuations in pressure can lead to dangerous situations, including leaks or explosions. Acetylene, for example, is highly sensitive to pressure changes and can become unstable if the pressure is not carefully regulated. A sudden surge in pressure could cause dangerous backfires or even a catastrophic event.
A pressure regulator prevents this by maintaining the pressure at safe levels, reducing the risk of accidents. Moreover, it ensures that the gases are delivered to the equipment without excessive force, which minimizes the chances of hose ruptures, valve malfunctions, or gas leaks.
How Pressure Regulators Enhance Safety:
- Prevents Explosions: Stable pressure ensures that combustible gases like acetylene are maintained at safe levels to avoid ignition or explosive reactions.
- Protects Workers: Operators working with high-pressure gases are shielded from hazardous situations by the consistent flow provided by the pressure regulator.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Regulatory bodies like OSHA and the NFPA have guidelines that mandate pressure regulators for safe welding and cutting practices.
3. Prevents Equipment Damage
Welding and cutting equipment can be costly, and keeping it in optimal working condition is crucial for long-term performance. Fluctuations in gas pressure can cause significant damage to sensitive components like torches, valves, and hoses. Excessive pressure can cause valves to leak, torches to malfunction, and hoses to burst.
A pressure regulator acts as a protective barrier, ensuring that the pressure does not exceed the safe operating range. By doing so, it prolongs the life of your equipment, reduces maintenance costs, and prevents downtime.
Preventing Equipment Damage:
- Consistent Gas Flow: Keeps gas pressure within the required range, reducing the likelihood of excessive strain on equipment.
- Extended Equipment Life: Protects hoses, torches, and regulators from wear caused by erratic pressure, saving on repair or replacement costs.
4. Enhances Weld Quality
The quality of the weld is directly influenced by the amount and type of gas used. If the pressure is too low, the weld may be weak or incomplete; too high a pressure can result in a rough, porous weld or even oxidation. The pressure regulator ensures the correct flow of gas, which in turn leads to cleaner, stronger welds.
For example, when using oxygen and acetylene for welding, the oxygen pressure needs to be precisely controlled to produce the proper flame characteristics for the task at hand. The regulator allows the operator to adjust the pressure to match the specific welding requirements, whether they are creating a fine bead or making a heavy-duty joint.
Impact of Pressure on Weld Quality:
| Pressure Too Low | Pressure Too High | Ideal Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Weak welds, poor fusion, lack of penetration | Excessive spatter, oxidation, rough surface | Optimal heat, clean weld, strong fusion |
| Incomplete fusion between materials | Poor flame control and instability | Consistent flame ideal for controlled welding |
5. Improves Cutting Precision
In cutting applications, gas pressure directly influences the quality and precision of the cut. Too high a pressure can lead to uneven cuts, excessive heat, or material distortion. Too low a pressure can result in slow, inefficient cutting and poor-quality edges.
A pressure regulator ensures that the right pressure is used to produce a clean, smooth cut with minimal material waste. Whether cutting metal, steel, or other materials, maintaining the correct gas pressure leads to faster, more accurate cuts and less rework.
Benefits for Cutting Precision:
- Consistent Flame: Provides a stable, consistent flame that improves cutting quality.
- Faster Cuts: By optimizing pressure, the process becomes more efficient, reducing cutting time and material waste.
6. Prevents Gas Wastage
When gas is not regulated properly, excess gas may be used, which leads to wastage and increased operational costs. A pressure regulator optimizes the gas flow, ensuring that only the necessary amount of gas is delivered to the welding or cutting equipment. This not only saves money but also reduces environmental impact.
How Pressure Regulators Reduce Gas Waste:
- Efficient Gas Usage: Prevents excessive flow, ensuring the exact amount of gas is used for each task.
- Cost Savings: Less gas wastage means reduced operational costs over time.
- Eco-Friendly: More efficient use of gas reduces carbon footprint and promotes sustainable practices in the industry.
7. Adapts to Various Gas Types
Different welding and cutting applications require different gases, each with its own pressure requirements. For example, oxygen requires a much higher pressure than acetylene or argon. A high-quality pressure regulator can be adjusted to accommodate the specific pressure needs of each gas.
Regulating Multiple Gases:
| Gas Type | Required Pressure | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | 30–50 psi (depending on application) | Used for cutting and welding, requires high pressure |
| Acetylene | 5–15 psi | Used for oxy-fuel welding, requires lower pressure |
| Argon | 50–150 psi | Used for TIG welding, requires specific pressure settings |
8. Regulates Multiple Gases Simultaneously
Many welding and cutting processes require a combination of gases. For example, in oxy-fuel welding or cutting, both oxygen and acetylene must be regulated separately but simultaneously. A dual-stage pressure regulator can control the pressure of multiple gases at the same time, ensuring the correct mixture and pressure levels are maintained.
Dual-Stage Pressure Regulators:
- Multiple Gas Control: Manages both gases independently, preventing mixture errors.
- Accurate Adjustments: Allows precise control over the gas mixture for specialized welding and cutting tasks.
9. Reduces Operator Fatigue
Handling gas pressure manually or adjusting pressure throughout the process can be mentally and physically taxing. A pressure regulator automates the pressure control, allowing the operator to focus on the task at hand without worrying about maintaining consistent pressure. This reduces operator fatigue and increases productivity.
10. Compliance with Industry Standards
Various safety regulations and standards, including those from OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and NFPA (National Fire Protection Association), mandate the use of pressure regulators in welding and cutting operations. These standards are designed to protect workers and ensure safe, efficient practices.
Key Industry Standards for Pressure Regulators:
- OSHA Guidelines: Require the use of pressure regulators for gas welding and cutting to reduce hazards.
- NFPA Codes: Specify pressure regulation for safety in welding and cutting environments.
FAQ
1. What types of pressure regulators are used in welding and cutting?
There are single-stage and dual-stage pressure regulators. Single-stage regulators are suitable for applications requiring consistent, low-pressure control, while dual-stage regulators are used for higher precision when controlling multiple gases or managing higher pressures.
2. How often should pressure regulators be maintained?
Pressure regulators should be inspected regularly for signs of wear, leaks, or damage. It is recommended to perform maintenance every 3 to 6 months, depending on usage and operating conditions.
3. Can I use the same pressure regulator for different gases?
Some regulators are designed for use with specific gases, while others can accommodate multiple gas types with the correct adjustments. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure compatibility.
4. Why is pressure regulation important for cutting precision?
Proper pressure ensures that the flame is stable and uniform, leading to more accurate and clean cuts. Inconsistent pressure can cause rough edges and poor cut quality.
References
- American Welding Society (AWS). (2019). Welding Handbook, Volume 1: Welding Science and Technology. American Welding Society.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021). Safety and Health Regulations for Welding, Cutting, and Brazing. U.S. Department of Labor.


 English
English  русский
русский  Español
Español